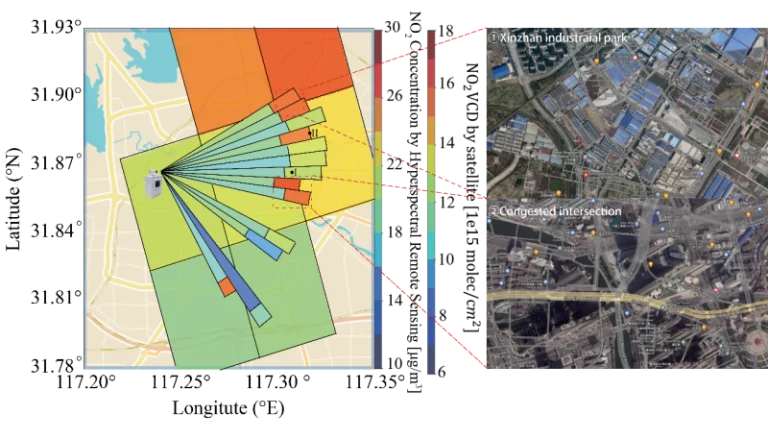
The Chinese Academy of Sciences has published a study in the Journal of Remote Sensing that introduces a hyperspectral remote sensing technique capable of hour-hectometer-level horizontal distribution of trace gases, offering an advanced tool to accurately identify emission sources.
This technique uses effective optical paths (EOPs) within the ultraviolet (UV) and visible (VIS) spectral bands to measure average trace gas concentrations across various distances. A novel aspect of the study is the application of the onion-peeling method, which refines the data to reveal concentrations at specific distances, offering heightened detail and accuracy.
The method represents a significant improvement over traditional satellite and in-situ monitoring techniques, which are often constrained by spatial and temporal resolution. In practical applications, this technique successfully pinpointed small, high-value emission areas in Hefei, China, demonstrating its potential for detailed environmental monitoring and urban planning. It also highlighted the limitations in the ability of satellite data to represent daily average concentrations, indicating the need for a reevaluation of current emission inventories. This research not only improves understanding of atmospheric pollutants and their distribution but also reportedly provides a powerful tool for more targeted pollution control strategies and environmental policymaking.
Chinese Academy of Sciences researcher Chuan Lu said, “This new method significantly outperforms existing ones in terms of spatial and temporal resolution, offering a detailed insight into the horizontal distribution of trace gases and enabling more accurate identification of high-value emission areas.”
This technique offers insights into urban pollution hot spots and helps identify high-value emission areas, which are crucial for urban planning and public health. It enhances the reliability of bottom-up emission calculations and informs strategies for pollution control and mitigation. The method’s capacity to provide higher resolution in emission source detection paves the way for more targeted and effective environmental policies and interventions. According to the researchers, its application has the potential to revolutionize the understanding of emission sources and make a significant contribution to global efforts in pollution control and environmental protection.
For more key remote sensing updates from the meteorological technology industry, click here.